Electroplating Process and Information
Electroplating or “plating” uses electricity to reduce dissolved metal cations to form metal coating on an electrode. The process allows for a metallic coating or finish to be applied to a metal, or conducting surface by using a current of electricity. Various items use electro plating such as keys, coins, and printing plates. Because of the different items that can be electroplated, there are different types of electroplating, like copper, silver, and chromium. Each of numerous types of electroplating will use different temperatures for the electrolyte bath, rinse, dip, and cleaner.
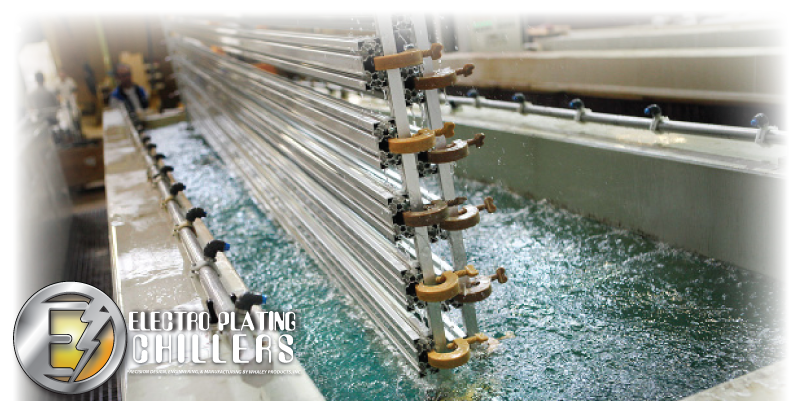
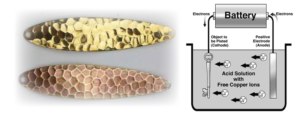
The process of the electroplating bath involves a diluted solution filled with electrolytes. The solution varies upon the chemical composition of the object being plated. Nickel plating solutions will differ from silver, and vice versa. The solution is used to allow an interaction between the two objects (cathode and anode). The cathode is the object that is going to be plated. The anode is the positive electrode item that is doing the plating. A battery is used to allow a current between the two pieces inside the mixed electrolyte solution. The battery allows for the loss and adding of electrons from the anode to the cathode.
Electroplating is used for different reasons, and used a variety of different process. Electroplating is used for appearance, protection, special surface properties, and engineering/mechanical properties. Because of the different applications, the solutions of electrolytes can vary. Some electrolytes are metal/molten salts, acids, or bases. Depending on the solution resistance, brightness, hardness, mechanical strength, wear resistance and corrosion will vary.
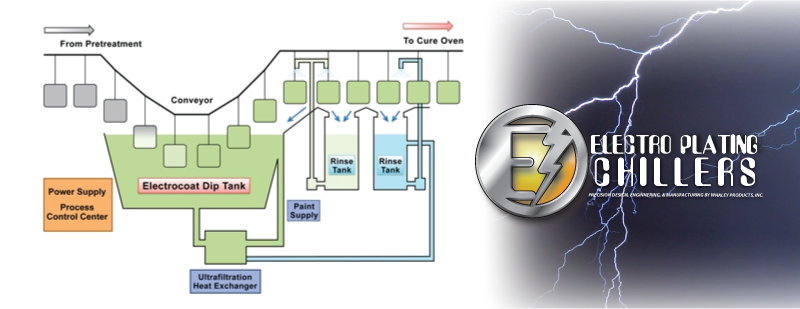
At an industrial or commercial scale, plating can happen in batches. These batches can happen in mass plating, rack plating, continuous plating, line plating, barrel plating, or barrel plating. In these batches the electrolyte solution can be hot or cold. Chillers can be used to maintain constant cooled temperatures by removing heat. The heat is removed by air or liquid. Cool water is needed to rinse the product, and plate the product.
 Packaged Chillers Non-expandable (integrated pump tank) 1.5Ton – 20Ton Single / Dual Circuits Single / Dual Pumps |
 SAE Series Modular Chillers Expandable (pump & tank on separate skid) 1.5Ton – 200Ton Single / Dual Circuits |
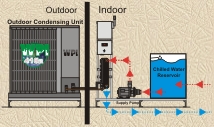 SAR Series Split Chillers Expandable (Outdoor Condensing Unit) (pump, tank, evaporator on indoor skid) 1.5Ton – 200Ton Single / Dual Circuits |